
Joel Collier, Ph.D.
AIMBE College of Fellows Class of 2017 For pioneering contributions to the design of immunologically active biomaterials.
New Vaccine Platform – With No Needles – Has Potential to Be More Effective With Fewer Side Effects
Via SciTech Daily | August 7, 2020Study shows that peptide nanofibers induce immune response in lungs and lymph nodes without requiring adjuvants for efficacy, indicating promise for new vaccine development.
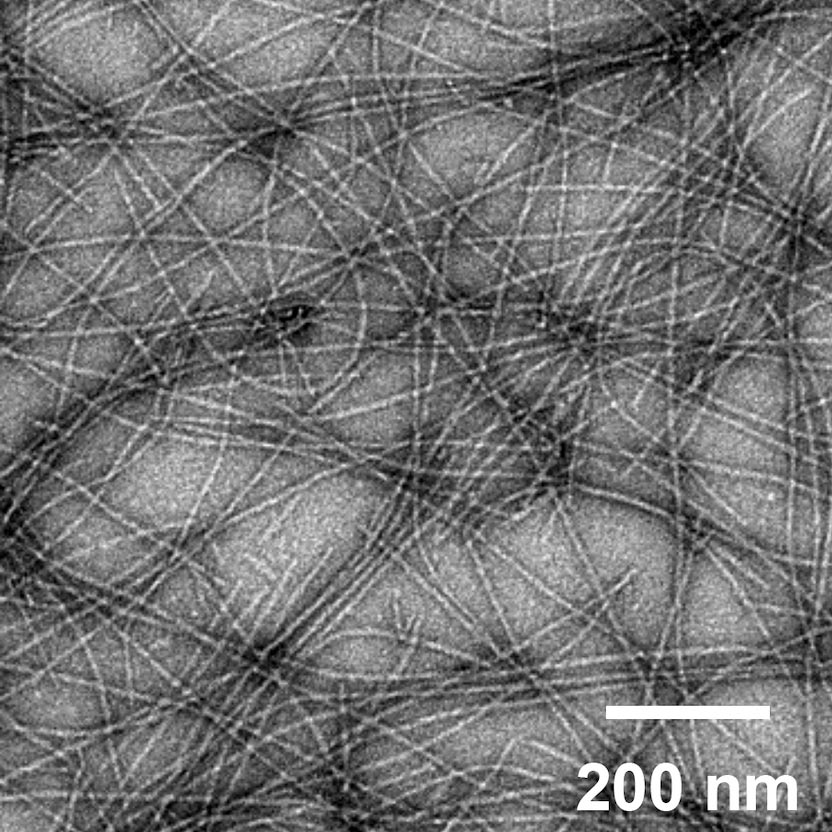
An image of self-assembled peptide nanofibers, which are currently under investigation for engineered vaccines. Credit: Collier Lab
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic is shining a bright spotlight on vaccine development. As numerous vaccines race through clinical trials, physicians and researchers continue to work on developing new vaccine technologies to generate the most effective vaccines with the fewest side effects.
A new proof-of-concept study by researchers at the University of Chicago and Duke University demonstrates the potential for one such platform, using self-assembling peptide nanofibers tagged with antigens to prime the immune system against a potential invasion.
Their research, published in Science Advances on August 7, 2020, showed that these nanofibers can induce an immune response and activate T cells without the use of additional adjuvants, which can induce inflammation and are associated with common vaccine side effects, like soreness at the injection site or low-grade fever… Continue reading.
Joel Collier, Ph.D. To be Inducted into Medical and Biological Engineering Elite
Via AIMBE | March 1, 2017WASHINGTON, D.C.— The American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering (AIMBE) has announced the pending induction of Joel Collier, Ph.D., Associate Professor, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Duke University, to its College of Fellows. Dr. Collier was nominated, reviewed, and elected by peers and members of the College of Fellows For pioneering contributions to the design of immunologically active biomaterials..
 AIMBE
AIMBE
